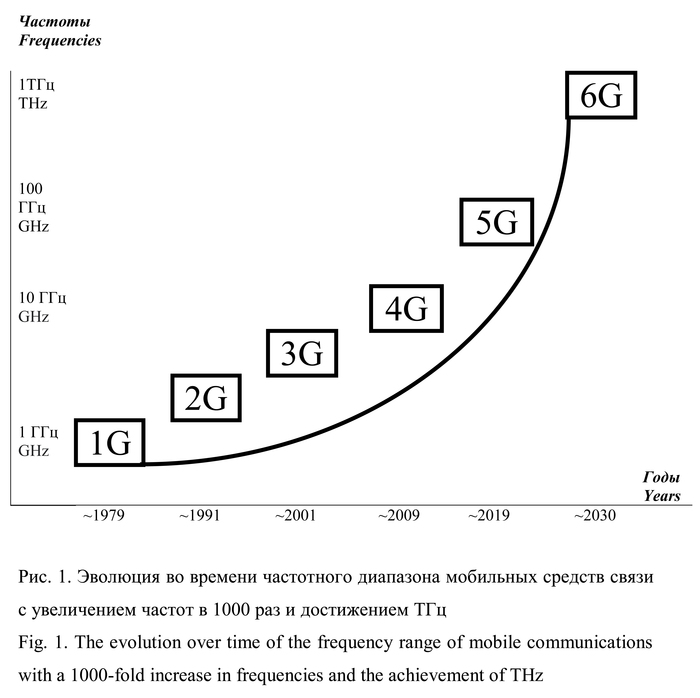
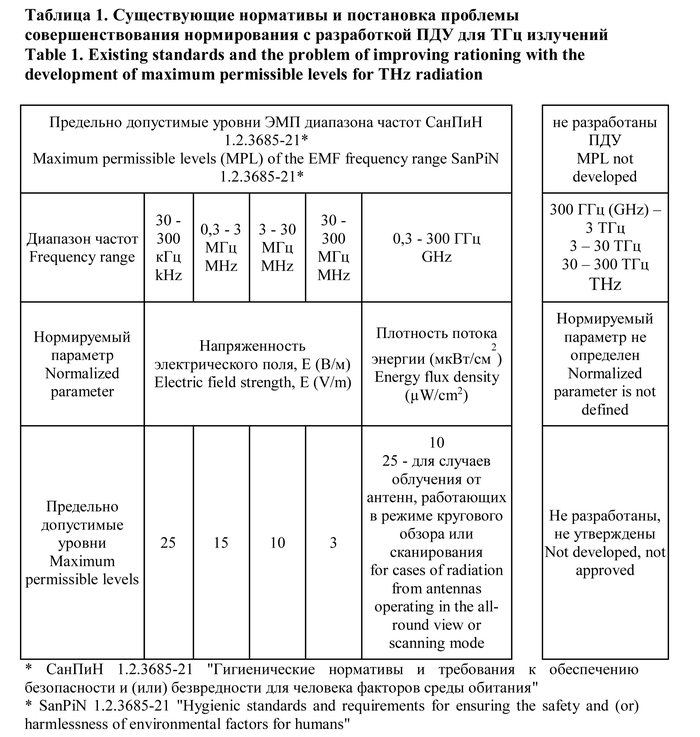
При распространённости применения в технологиях терагерцевых излучений, актуально изучение их влияния на здоровье, измерения и разработка нормативов предельно допустимых уровней (ПДУ). Цель исследования — постановка проблемы распространённости терагерцевых излучений, актуальности измерений и нормирования их влияния на человека. Проанализированы имеющиеся данные по перспективам распространения в технологиях терагерцевых излучений, по воздействию терагерцевых излучений на здоровье, ПДУ электромагнитных полей различного диапазона частот в санитарных правилах и нормах (СанПиН). Ряд исследований подтверждают влияние терагерцевых излучений на биологические объекты на молекулярном, клеточном и органном уровнях; не разработано, не утверждено нормирование ПДУ терагерцевых излучений.
Целесообразны разработка нормирования, определения и утверждения ПДУ терагерцевых излучений для обеспечения безопасности в медицине труда, медицинской физике, сохранении здоровья в среде обитания и профессионального здоровья на производстве.
1. Radio Regulations. Geneva: ITU; 2024.
2. Bratman V.L., Litvak A.G., Suvorov E.V. Mastering the terahertz domain: sources and applications. Phys. Usp. 2011; 54: 837–44 https://doi.org/ 10.3367/UFNe.0181.201108f.0867 (in Russian)
3. TeraHertz technology (THz); RF Hardware Modeling. Sophia-Antipolis, France: ETSI; 2025.
4. Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russia 02.05.2023 No. 206n "On Approval of Qualification Requirements for medical and pharmaceutical workers with higher education" (In Russian).
5. Castilla, S., Terrés, B., Autore, M., et al. Fast and sensitive terahertz detection using an antenna-integrated graphene pn junction. Nano letters. 2019; 19 (5): 2765-73. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04171
6. Valušis, G., Lisauskas, A., Yuan, H., Knap, W., & Roskos, H. G. Roadmap of terahertz imaging 2021. Sensors. 2021; 21 (12): 4092. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124092
7. Molter, D., Ellenberger, K. S., Klier, J., Duran, S., Jonuscheit, J., von Freymann, G., ... & Deninger, A.. Kilohertz pixel-rate multilayer terahertz imaging of subwavelength coatings. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12 (10): 4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104964
8. Kohlhaas R.B., Breuer S., Mutschall S., et al. Ultrabroadband terahertz time-domain spectroscopy using III-V photoconductive membranes on silicon. Optics Express. 2022; 30 (13): 23896-908. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.454447
9. Agarwal H., Nowakowski K., Forrer A., et. Al. Ultra-broadband photoconductivity in twisted graphene heterostructures with large responsivity. Nature Photonics. 2023; 17 (12): 1047-53. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-023-01291-0.
10. Terahertz radiation systems: Technologies and global markets. Wellesley, USA: BCC Research; 2023.
11. 6G: The Next Horizon From Connected People and Things to Connected Intelligence Edited by Wen Tong , Peiying Zhu. Cambridge University Press; 2021.
12. Kim M.J., Eom D., Lee, H. The geopolitics of next generation mobile communication standardization: The case of open RAN. Telecommunications Policy. 2023; 47(10): 102625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2023.102625
13. Hardell L., Carlberg M. Health risks from radiofrequency radiation, including 5G, should be assessed by experts with no conflicts of interest. Oncol Lett. 2020 Oct; 20(4):15. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.11876.
14. International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. A Description of ICNIRP’S Independent, Best Practice System of Guidance on the Protection of People and the Environment from Exposure to Non-Ionizing Radiation. Health Physics. 2022; 122 (5): 625-8. https://doi.org/10.1097/HP.0000000000001561
15. Framework for Developing Health-Based EMF Standards. Geneva: WHO. 2006.
16. Model legislation for electromagnetic fields protection. Geneva: WHO. 2006.
17. WHO research agenda for radiofrequency fields. Geneva: WHO. 2010.
18. Movsisyan M., Al-Rossais A. A., Sayeed S., Movsisyan G. Applications of terahertz waves in medical diagnostics: A literature review. International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health. 2024; 11 (6): 2450. https://doi.org/10.18203/2394-6040.ijcmph20241512
19. Liu Y. C. et al. Safety profiles of terahertz scanning in ophthalmology. Scientific Reports. 2021; 11 (1): 2448. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-82103-9
20. Smolyanskaya O.A., Chernomyrdin N.V., Konovko A.A., et al. Terahertz biophotonics as a tool for studies of dielectric and spectral properties of biological tissues and liquids. Progress in Quantum Electronics. 2018; 62: 1-77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pquantelec.2018.10.001
21. Musina G.R., Nikitin P.V., Chernomyrdin N.V., et al. Prospects of terahertz technology in diagnosis of human brain tumors – A review. Journal of Biomedical Photonics & Engineering. 2020; 6 (2): 020201. https://doi.org/10.18287/jbpe20.06.020201
22. Cherkasova O., Peng Y., Konnikova M., et al. Diagnosis of glioma molecular markers by terahertz technologies. Photonics. 2021; 8 (1): 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8010022
23. Pu Z., Wu Y., Zhu Z., Zhao H., Cui D. A new horizon for neuroscience: terahertz biotechnology in brain research. Neural Regeneration Research. 2025; 20 (2): 309-325. https://doi.org/10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-00872
24. Gezimati M., Singh G. Terahertz imaging and sensing for healthcare: current status and future perspectives. Ieee Access. 2023; 11:18590-18619. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3247196
25. Svistunov A.A., Tsymbal A.A., Litvitsky P.F., Budnik I.A. Experimental and clinical substantiation of the use of electromagnetic waves of the terahertz range at frequencies of radiation and absorption of nitric oxide and oxygen in various forms of pathology. Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. 2017; 72 (5): 365–374. https://doi.org/10.15690/vramn817 (in Russian)
26. Amini T., Jahangiri F., Ameri Z., et al. A review of feasible applications of THz waves in medical diagnostics and treatments. Journal of Lasers in Medical Sciences. 2021; 12: e92. https://doi.org/10.34172/jlms.2021.92
27. Nikitkina A.I., Bikmulina P.Y., Gafarova E.R. Terahertz radiation and the skin: a review. Journal of Biomedical Optics. 2021; 26 (4): 043005. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.jbo.26.4.043005
28. Zhang J., Liu C., Lü J., Xu R., Le, W. Terahertz technology: A new frontier in Alzheimer’s disease therapy. The Innovation Life. 2024 2(3): 100084-1. https://doi.org/10.59717/j.xinn-life.2024.100084
29. Smolyanskaya O.A., Zaytsev K.I., Dolganova I.N., et al. Tissue optical clearing in the terahertz range. In Handbook of Tissue Optical Clearing (pp. 445-458). USA, Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2022. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003025252-28
30. Wilmink G.J., Grundt J.E. Invited Review Article: Current State of Research on Biological Effects of Terahertz Radiation. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves. 2011; 32 (2), 1074–1122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-011-9794-5
31. Zhang D. Interaction Between Terahertz Wave and Biomolecules. In: Chang C., Qi F., Zhang L., Hou L. (eds) Proceedings of the 2025 China National Conference on Terahertz Biophysics. CTB 2024. Springer Proceedings in Physics, vol 423. Singapore: Springer; 2025. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-4886-3_35
32. Song Z., Xue L., Ouyang Q. et al. Impact of a Terahertz electromagnetic field on the ion permeation of potassium and sodium channels. Communication Chemistry. 2025; 8, article number 101. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-025-01503-4
33. Nikitkina A.I., Bikmulina P.Y., Gafarova E.R., Kosheleva N.V., et al. Terahertz radiation and the skin: a review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2021; 26 (4): 043005. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JBO.26.4.043005.
34. Shirkavand A., Tuchin V.V., Jahangiri F. Mohajerani E. A review on terahertz non-destructive applications for wound and diabetic foot screening. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2022; 54 (8): 467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-03828-z
35. Cherkasova O.P., et al. Mechanisms of the effect of terahertz radiation on cells. Optics and spectroscopy. 2020. 128 (6): 852–64. https://doi.org/10.21883/OS.2020.06.49420.51-20 (in Russian)
36. Yamazaki S., Harata M,, Ueno Y,, Tsubouchi M,, Konagaya K,, et al. Propagation of THz irradiation energy through aqueous layers: Demolition of actin filaments in living cells. Sci Rep. 2020; 10 (1): 9008. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65955-5.
37. Shaoqing M., Zhiwei L., Shixiang G., Chengbiao L., Xiaoli L., Yingwei L. The laws and effects of terahertz wave interactions with neurons. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023; 11: 1147684. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2023.1147684
38. Rytik A.P., Tuchin V.V. Effect of terahertz radiation on cells and cellular structures. Front. Optoelectron. 2025; 18 (2): 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-024-00146-y
39. Sacco G., Zhadobov M. Physical Interactions Between Millimeter Waves and Human Body: From Macro- to Micro-Scale. IEEE Journal of Microwaves. 2024; 4 (3): 318-328. https://doi.org/10.1109/JMW.2024.3407712.
40. Wongkasem N. Electromagnetic pollution alert: Microwave radiation and absorption in human organs and tissues. Electromagnetic biology and medicine. 2021; 40 (2): 236 – 253. https://doi.org/10.1080/15368378.2021.1874976
41. Grigoriev O., Goshin M., Prokofyeva А., Alekseeva V. Features of national policy in approaches to electromagnetic field safety of radio frequencies radiation in different countries. Hygiene and Sanitation. 2019; 98(11): 1184-1190. http://dx.doi.org/ 10.18821/0016-9900-2019-98-11-1184-1190 (In Russian).
42. Controlling limits for electromagnetic environment. National Standard of the People’s Republic of Chine GB 8702-2014. Ministry of Environmental protection of the People’s Republic of Chine. 2014.
43. IEEE Standard for Safety Levels with Respect to Human Exposure to Electric, Magnetic, and Electromagnetic Fields, 0 Hz to 300 GHz. IEEE Std C95.1-2019 (Revision of IEEE Std C95.1-2005/Incorporates IEEE Std C95.1-2019/Cor 1-2019). 2019: 1-312. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEEESTD.2019.8859679.
44. Limits of human exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic energy in the frequency range from 3 kHz to 300 GHz. Consumer and Clinical Radiation Protection Bureau Environmental and Radiation Health Sciences Directorate, Healthy Environments and Consumer Safety Branch, Health Canada: 2015.
45. ICNIRP guidelines for limiting exposure to electromagnetic fields (100 kHz to 300 GHz). Health Phys 2020; 118(5): 483–524. https://doi.org/10.1097/HP.0000000000001210
46. International EMF Project: investigates health effects of electromagnetic elds, advises national authorities on EMF radiation protection. Geneva: WHO; 2005.
47. International Commission on the Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields (ICBE-EMF). Scientific evidence invalidates health assumptions underlying the FCC and ICNIRP exposure limit determinations for radiofrequency radiation: implications for 5G. Environ Health. 2022; 21 (1):92. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-022-00900-9.